Phonetics (1)
The study of the medium of spoken language usage, in all its aspects and all its varieties, constitutes the subject of Phonetics. Phonetics is concerned with the medium in speaking all human languages (…) and as used in all styles of speech (…)
Abercrombie (1967: 2).
Phonetics is the systematic study of human speech sounds. It provides a means of describing and classifying virtually all the sounds that can be produced by human vocal tracts.
Catford (1988: 1)
Phonetics (2)
Phonetics is concerned with describing the speech sounds that occur in the languages of the world. We want to know what these sounds are, how they fall into patterns, and how they change in different circumstances. Most importantly, we want to know what aspects of the sounds are important for conveying the meaning of what is being said.
(Ladefoged 1975: 1)
… the indispensible foundation…
(Sweet 1877/1913: 85)
The International Phonetic Association
Founded 1886
Aim: "To promote the study of the science of phonetics and the various practical applications of that science."
International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA)
Extended IPA (ExtIPA) for the transcription of disordered speech
Handbook (1948), Handbook (1949)
Illustrations of the IPA (in the Handbook)
Journal of the IPA twice-yearly
Sponsors major conferences
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA)
Theoretical assumptions (Handbook 1999: 3ff):
- Some aspects of speech are linguistically relevant, whilst others (such as personal voice quality) are not
- Speech can be represented partly as a sequence of discrete sounds or ‘segments’
- Segments can usefully be divided into two major categories, consonants and vowels
- The phonetic description of consonants and vowels can be made with reference to how they are produced and their auditory characteristics
- A number of ‘supersegmental’ aspects of speech, such as stress and tone, need to be represented independently of the segments
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA)
The development of the IPA follows a set of principles.
- A set of symbols for representing all possible sounds of the world’s languages
- Typographical concerns:
- Letters have a roman shape as far as possible
- Italics, bold etc. are not used as the basis for new symbols
- For each distinctive sound in a language, there should be one symbol
- Diacritics should be avoided where possible
- Phonetic transcriptions should be enclosed in [square brackets]
- A transcription is comopsed of a set of symbols accompanied by a set of conventions for their interpretation
The Vocal Tract (mid-sagittal section)
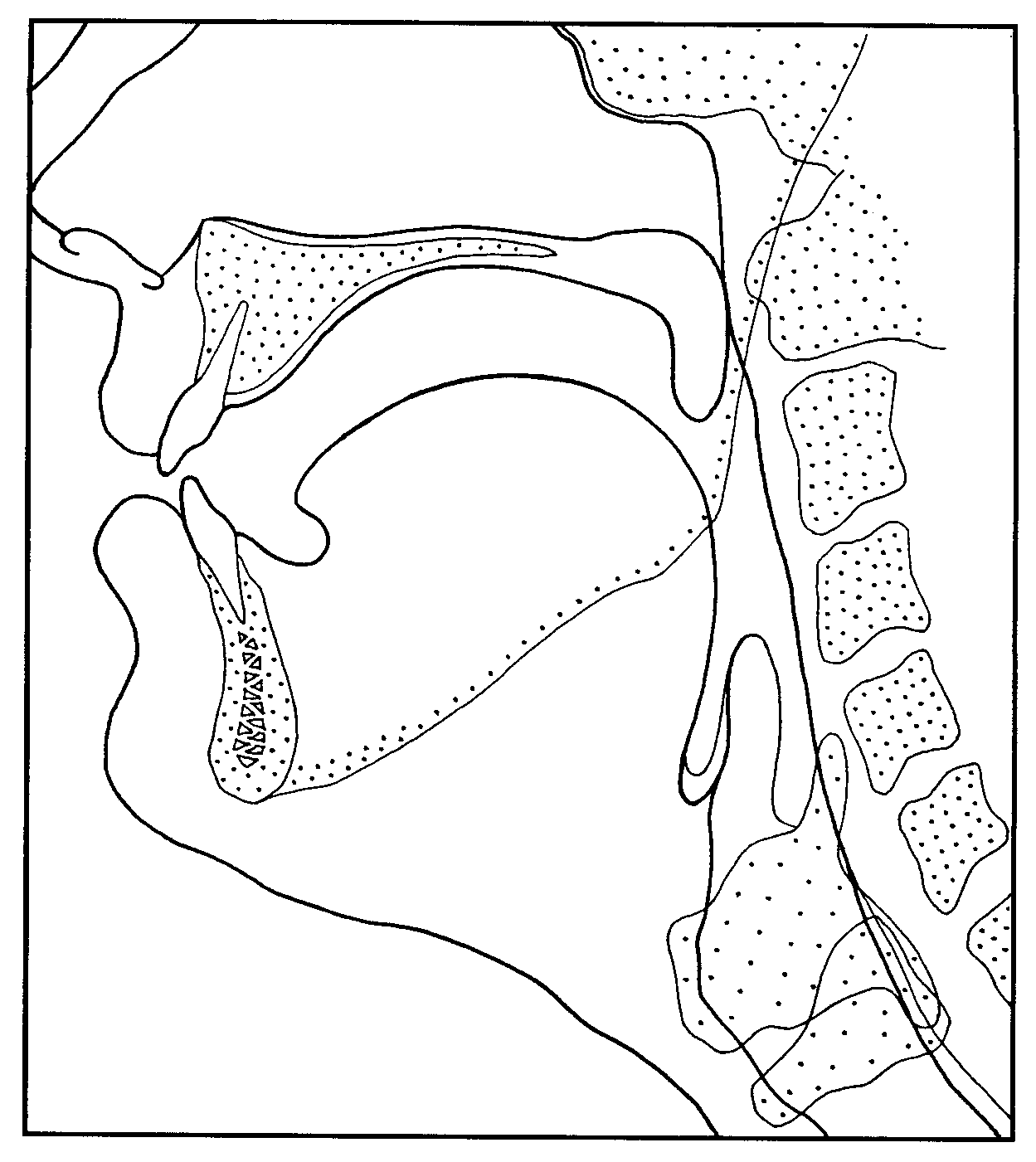
Taken from Laver (1994: ix)

