Advanced electron energy loss spectroscopy inside
Electron Microscopes
Electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) measures the probability of energy
loss of an electron beam after it has transversed through a sample. The fine structure in EELS contains a
wealth of information about the sample and can be data-mined to know not only
the chemical composition, but also chemical bonding as well as local electronic
structure of materials. The
information deduced is similar to that available in photo-absorption
spectroscopy, but EELS has the advantage of a broad energy range, covering from
optical to UV and further to X-ray wavelength, and
atomic scale resolution because the ability of focusing electron beams using
electromagnetic lenses. Our aim is
to develop the EELS inside Electron Microscope to study the spatially resolved
chemical, bonding and electronic information of materials in nanoscales. We have a broad range of research activities,
from novel instrumental development, to new methodology and ab-initio
simulation of fine structures.
XL
Multivariate
statistical analysis of electron energy-loss spectroscopy in anisotropic
materials
Ultramicroscopy,
108, 465 (2008)
YK SUN AND J YUAN
Electron Energy Loss
Spectroscopy of Core-electron Excitation in Anisotropic Systems: Magic angle,
Magic Orientation and Dichroism
Phys. Rev. B 71, 125109-125119 (2005).
J ZHU, SP GAO, AH ZHANG, AND J YUAN
Theoretical
Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy and its Application in Materials Research
J. Electron Microscopy, 54(3), 293-298 (2005).
YK SUN AND J YUAN
Spatially
Resolved Core Level Spectroscopy of Nanotube
Materials Science Forum, 475-479, 4085-4088 (2005).
SP GAO, J ZHU, AND J YUAN
Identification
of Polymorphs of sp3 Bonded Carbon and Boron Nitride Using
Core-level Absorption Spectroscopy
Chem. Phys. Lett. 400(4-6), 413-418 (2004).
SP GAO, J JIANG, MH CAO, J ZHU, J YUAN
Unoccupied Electronic States
in CaB6 Studied by Density Functional Theory and EELS Measurements
Phys. Rev. B 69, 214419 (2004).
SP GAO, A ZHANG, J ZHU, J YUAN
Anisotropic
Spectroscopy of Nitrogen K-Edge in Group III Nitrides
Appl. Phys. Lett., 84, 2784 (2004).
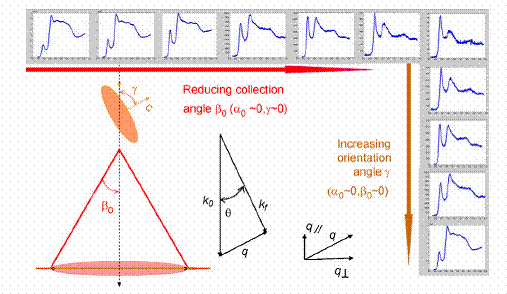
An illustration of strong dependence of the
EELS fine structure as a function of specimen orientation and collection
condition used inside an electron microscope.
The example is taken from Carbon 1s absorption from graphite. To overcome this uncertainty in relative
intensity of the spectral fine structure, we have developed methods in which
either the spectra fine structure are invariant against
specimen orientation (magic angle electron energy loss spectroscopy, or MAEELS)
or against collection conditions (magic orientation electron energy loss
spectroscopy, MOEELS). MAEELS is particularly
suitable for nanoscale analysis.
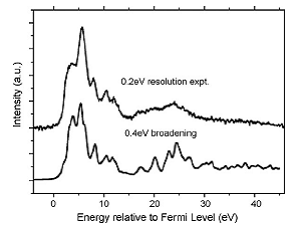
A comparison of experimental EELS spectrum (Nitrogen K-edge absorption,
background and Nitrogen 1s level binding energy subtracted) and the theoretical
spectrum generated using a modified DECAPO electronic structure simulation code
(Yuan 2008).