1. Quantum Phenomena#
Introduction
In the early 1900 the ultraviolet catastrophe was the first indication that not all was right in the world of physics. You may have studied the blackbody radiation curve shown in Figure 1.1 in the lab, an astrophysics course or previously in your A-level physis course.
The blackbody radiation curves given in Figure 1.1 show that the intensity of electromagnetic radiation from a blackbody emitter reduces at small wavelengths. This result is in contrast to the classical prediction that the intensity will rise asymptotically as the wavelength reduces towards zero. This phenomena is sometimes called the ultraviolet catastrophe due to the discrepancy between the theoretical prediction and expterimental evidence being greatest in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum and is considered one of the ealiest pieces of evidence that classical mechanics was not sufficent to describe the behaviour of photons. Planck resolved this discrepancy by assuming (with no experimental evidence or good theoretical reason) that the energy of the electromagnetic waves must be quantised in some way. With this correction Planck made the theory match the experimental data. This assumption by Planck lead to a revolution in physics out of which developed Quantum Physics and will be the focus of this course.
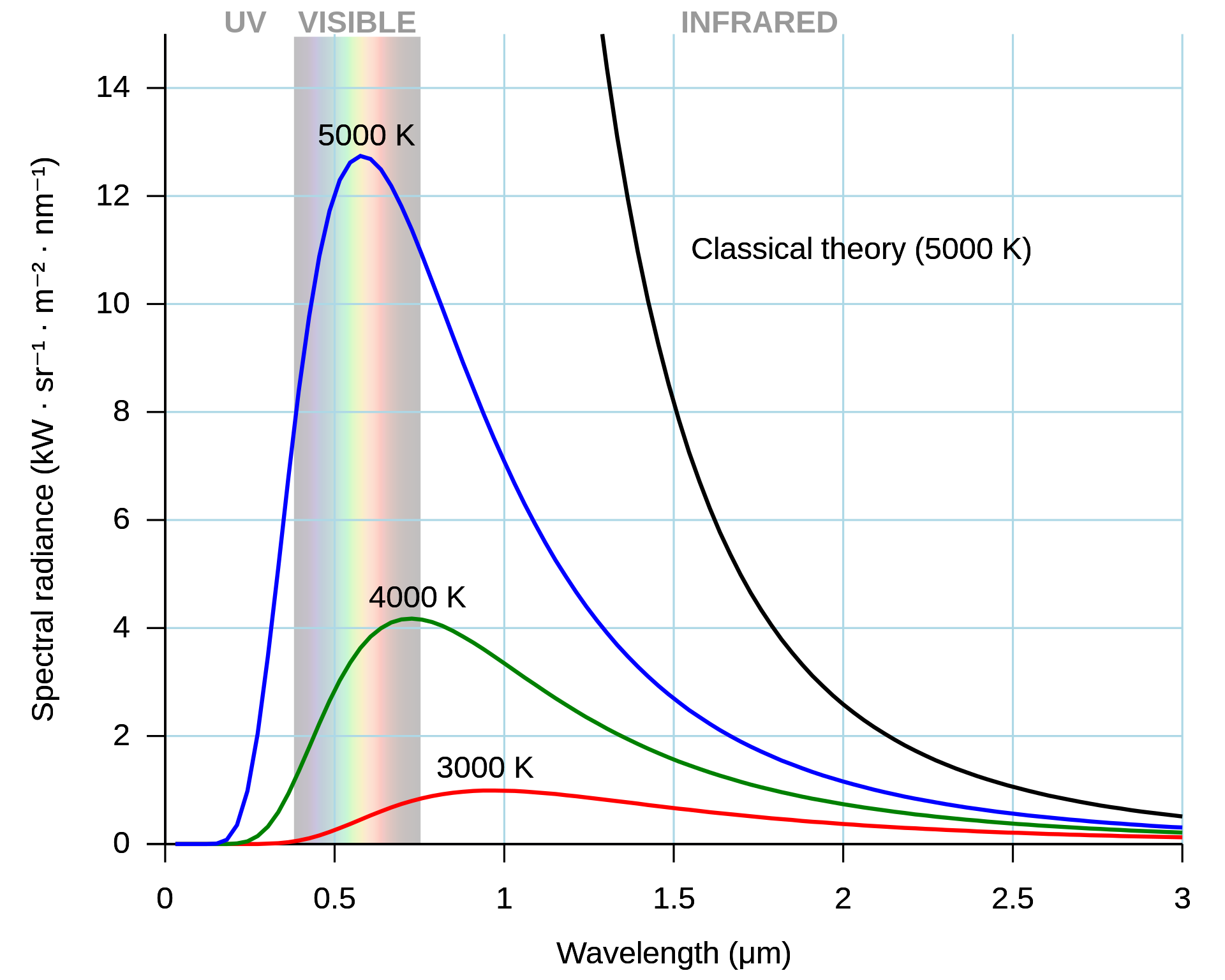
Fig. 1.1 The ultraviolet catastrophe is the error at short wavelengths in the Rayleigh–Jeans law (depicted as “classical theory” in the graph) for the energy emitted by an ideal black body. The error, much more pronounced for short wavelengths, is the difference between the black curve (as classically predicted by the Rayleigh–Jeans law) and the blue curve (the measured curve as predicted by Planck’s law).#
Outline of course content
The first lectures in the course will outline a series of quantum phenomena. The deviation from classical results will be explored and an emphasis will be placed on developing models that will allow you to make a physical interpretation of results from the Quantum Mechanics part of the course that will be delivered later in the term.
Initially we will focus on wave-particle duality first looking at the experimental evidence for how electromagnetic (EM) radiation interacts with matter. This will focus on four pieces of experimental evidence for the photonic (particle) nature of EM radiation. These are
The photoelectric effect,
Compton Scattering,
X-ray production.
Other evidence exists, for example pair production which you are encouraged to explore on your own, but will be considered outside the scope of this course for assessment.
We will then introduce and review the experimental evidence for the de Broglie hypothysis for the wave-like behaviour of particles. This will focus on experimental evidence from
The Davisson Germer experiment (electron diffraction).
Electron emission spectra.
We will use this phenomena to introduce the mathematical formalism for a treating a particle as a wave. This will rely of your knowledge of waves along with the de Broglie and Einstein relationships. With a wave-like formalism for particles we will introduce the Uncertainty Principle in both the momentum-position and energy-time forms. Finally we will conclude the review of the experimental evidence by looking at atomic structure and the Bohr model. This will be followed by an introduction to Quantum wave mechanics which can be found in chapter 2 of these notes.
